The Marinera Seizure: A Dangerous Escalation in Venezuela Sanctions Enforcement
Published
- 3 min read
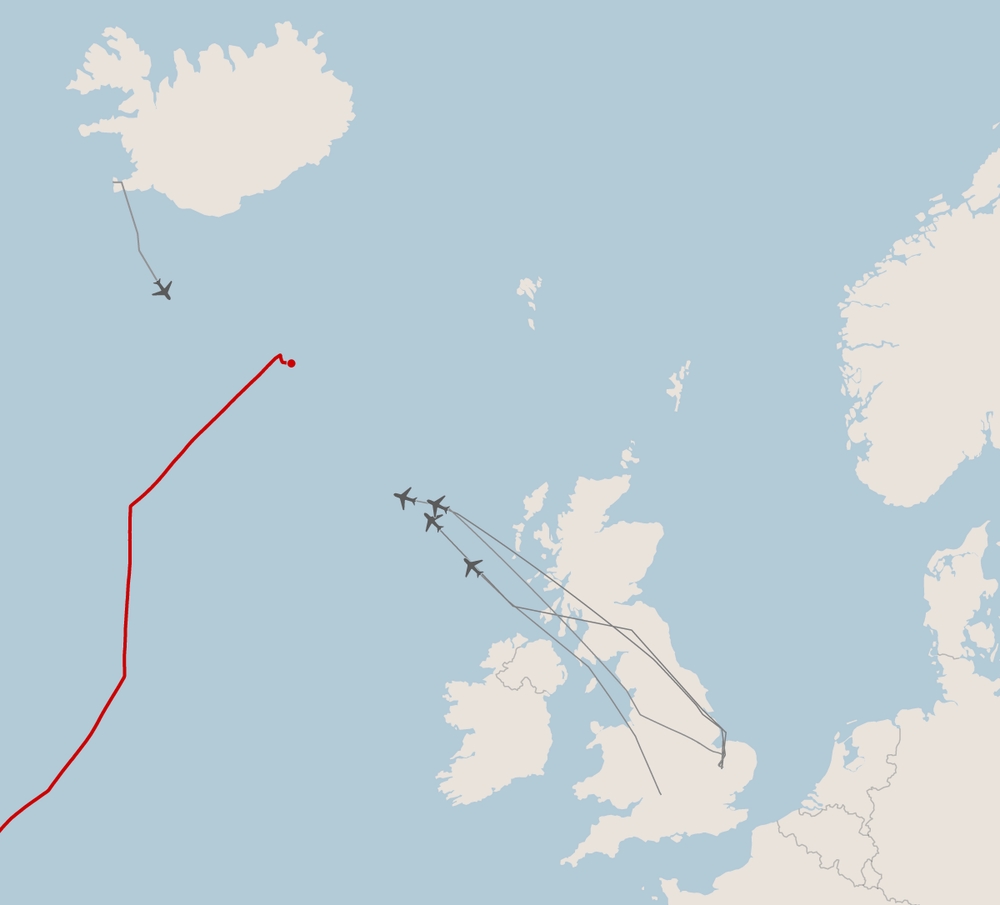
The Facts: A Naval Confrontation in the North Atlantic
On Wednesday, the United States Coast Guard, with significant military support, seized the oil tanker Marinera (formerly known as Bella 1) in the North Atlantic after a pursuit lasting more than two weeks. The vessel, which had recently been re-registered under the Russian flag, was intercepted in Iceland’s exclusive economic zone while attempting to evade U.S. sanctions enforcement against Venezuela’s energy exports. According to U.S. officials who spoke on condition of anonymity, the boarding occurred without Russian naval presence, averting a potential armed standoff between the two nuclear powers.
The operation involved substantial military assets, including Navy P-8 submarine-hunting aircraft and AC-130 gunships, with several aircraft departing from British bases to support the Coast Guard. Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem characterized the Marinera’s actions as “a desperate and failed attempt to escape justice,” while White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt indicated that crew members could face legal action in the United States.
Simultaneously, U.S. forces boarded another tanker, the M Sophia, in international waters near the Caribbean. This vessel, operating without a valid national flag according to the International Maritime Organization, was carrying approximately 1.8 to 2 million barrels of Venezuelan crude. The M Sophia had employed sophisticated deception tactics, including spoofing transponder signals to conceal its movements and using false identities when transporting oil to China.
The Context: Escalating Pressure on Venezuela
These seizures represent the most aggressive enforcement to date of President Trump’s announced “complete blockade” on oil tankers under sanctions traveling to and from Venezuela. The actions follow the capture of Venezuelan leader Nicolás Maduro on Saturday and appear designed to intensify pressure on his successor, Delcy Rodríguez, by cutting off the oil revenue that powers Venezuela’s economy.
Energy Secretary Chris Wright stated that the United States intends to oversee the sale of Venezuela’s oil production “indefinitely,” while Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth declared that “the blockade of sanctioned and illicit Venezuelan oil remains in FULL EFFECT — anywhere in the world.” Britain provided support for the Marinera operation, with Defense Secretary John Healey describing the vessel as “part of a Russian-Iranian axis of sanctions evasion which is fueling terrorism, conflict and misery from the Middle East to Ukraine.”
Both vessels are part of what analysts call a “shadow fleet” that transports oil for Russia, Iran, and Venezuela in violation of international sanctions. The Marinera specifically had a history of transporting Iranian oil for groups linked to terrorism, according to U.S. officials, which formed the basis for a federal seizure warrant issued last month.
The Russian Response and Legal Implications
Russia’s response to the seizure of a vessel flying its flag has been notably muted despite strong rhetoric from some lawmakers. The Russian Ministry of Transport stated that it had lost contact with the Marinera and emphasized that according to the 1982 U.N. Convention on the Law of the Sea, “no state has the right to use force against vessels duly registered in the jurisdictions of other states.” While the United States has not ratified this convention, it generally recognizes its provisions as customary law.
Pro-Russian Ukrainian politician Oleg Tsaryov, who claims to know the Marinera’s owner, asserted that “an attack on a Russian-registered ship is an attack on Russian territory” from a legal perspective. Russian lawmakers Andrei Klishas and Aleksei Zhuravlev accused the United States of “outright piracy on the high seas” and suggested the seizure could be classified as “a full-fledged military invasion of Russia.”
A Dangerous Precedent: My Assessment of the Marinera Operation
While supporting democracy and opposing authoritarian regimes like Maduro’s Venezuela is undoubtedly in America’s interests, the methods employed in the Marinera seizure raise profound concerns about proportionality, international law, and the dangerous escalation of economic sanctions into military confrontations.
The deployment of AC-130 gunships and submarine-hunting aircraft for what is essentially a law enforcement operation against an unarmed civilian vessel represents a troubling militarization of sanctions enforcement. Such overwhelming force, deployed against a ship with Russian and Ukrainian crew members in international waters, creates unacceptable risks of miscalculation and escalation between nuclear powers. The potential for a deadly confrontation that could spiral into broader conflict should give every sober-minded observer pause.
From a legal perspective, while the United States has legitimate interests in enforcing sanctions against regimes that threaten global security, the boarding of a vessel flying another nation’s flag in international waters without that nation’s consent establishes a dangerous precedent. If the United States claims this right, what prevents other nations from similarly intercepting U.S.-flagged vessels they believe violate their domestic laws? The principles of freedom of navigation and maritime sovereignty that America has long championed become undermined by such actions.
The tepid Russian response likely reflects Moscow’s current interest in maintaining relations with the Trump administration, particularly regarding Ukraine negotiations. However, we should not mistake tactical restraint for acceptance of this precedent. Russia and other nations will undoubtedly note this action and may employ similar tactics in the future against U.S. interests, citing the Marinera seizure as justification.
The Broader Implications for Global Order
This incident exemplifies the troubling trend toward the weaponization of economic interdependence and the extension of domestic law enforcement into international spaces. While combating terrorism financing and opposing authoritarian regimes are vital goals, the means must be proportionate and consistent with the international legal framework that has maintained relative peace and stability since World War II.
The concept of a “shadow fleet” operating outside international regulations certainly poses challenges to the rules-based order. However, the appropriate response involves multilateral cooperation through international organizations, enhanced intelligence sharing, diplomatic pressure on flag states, and coordinated port denials—not unilateral military actions that risk direct confrontation between major powers.
Furthermore, the humanitarian consequences of such aggressive sanctions enforcement cannot be ignored. While targeting the Maduro regime’s revenue streams is legitimate, the collateral impact on the Venezuelan people—already suffering from extreme economic hardship—must be carefully considered. Comprehensive sanctions regimes often inflict the greatest harm on civilian populations while failing to achieve their political objectives.
Principles Over Partisanship: A Call for Prudence
As someone deeply committed to democracy, freedom, and the rule of law, I believe the United States must champion these values through means that themselves respect international norms and legal principles. Our nation’s strength has historically derived not just from our military power but from our moral authority and commitment to a rules-based international system.
The Marinera operation, while technically successful in seizing the vessel, risks undermining that moral authority and setting precedents that may ultimately harm American interests. The use of military assets for sanctions enforcement, the boarding of vessels flying foreign flags in international waters, and the escalation of economic measures into naval confrontations represent a dangerous path that could erode the very international order we seek to preserve.
Instead, the United States should pursue multilateral approaches to sanctions enforcement, work through international maritime organizations to address registry abuses, and employ diplomatic tools to build coalitions against sanctions evasion. We must remember that our methods define us as much as our objectives, and that safeguarding democracy requires respecting the very principles we claim to defend.
The seizure of the Marinera may seem like a tactical victory in the short term, but we must carefully consider its strategic implications for international law, great power relations, and America’s standing as a nation that champions freedom through lawful means rather than mere force.
